In today’s world, 3D scanning has become a vital tool in various industries, including manufacturing, architecture, and healthcare. The technology has advanced significantly over the years, with two of the most common types of 3D scanning being laser 3D scanning and structured light 3D scanning. In this article, we will explain what these two types of 3D scanning are, their applications, and compare their pros and cons.
Laser 3D Scanning
Laser 3D scanning technology involves using a laser beam to project onto the object’s surface and measuring the reflection of the laser. This process captures precise details and can scan a wide range of surfaces, from reflective to dark surfaces. Laser 3D scanning is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and engineering for quality control, reverse engineering, and prototyping.
One of the significant benefits of laser 3D scanning technology is its ability to provide highly accurate measurements. The technology is ideal for measuring objects with complex shapes and provides a level of precision that cannot be achieved with traditional measurement techniques. Furthermore, laser 3D scanning is efficient and can capture a large amount of data in a relatively short period, making it an excellent option for high-volume applications.
However, there are also some disadvantages associated with laser 3D scanning technology. First, the laser beam can be hazardous to the human eye, which means that safety precautions must be taken when using this technology. Additionally, laser 3D scanning requires a stable environment, which can limit its use in certain applications.
Structured Light 3D Scanning
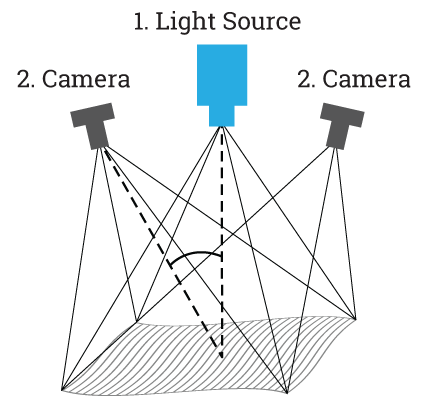
Structured light 3D scanning, also known as white light scanning, is a non-contact method of 3D scanning that involves projecting a structured light pattern onto the object’s surface and capturing the reflection with one or more cameras. The captured images are then processed to create a 3D model. This technology is ideal for capturing the details of an object’s surface and is commonly used in industries such as art, archaeology, and dental restoration.
One of the significant benefits of structured light 3D scanning technology is its ability to capture fine details with high accuracy. It is perfect for creating 3D models of objects with complex geometries and intricate surfaces. Additionally, structured light 3D scanning is a safe technology to use as it does not emit hazardous radiation.
However, structured light 3D scanning also has some limitations. It is not suitable for scanning dark surfaces as the structured light pattern may not be visible. Additionally, the accuracy of structured light 3D scanning is lower than that of laser 3D scanning.
Comparison of Laser 3D Scanning and Structured Light 3D Scanning
When it comes to comparing laser 3D scanning and structured light 3D scanning, there are several factors to consider. Both technologies have their unique strengths and weaknesses that make them suitable for different applications.
Laser 3D scanning is more accurate than structured light 3D scanning and can scan a wider range of surfaces. It is ideal for measuring objects with complex geometries and is widely used in quality control and reverse engineering applications. However, laser 3D scanning requires a stable environment and is not suitable for scanning dark surfaces.
Structured light 3D scanning, on the other hand, is perfect for capturing surface details with high accuracy. It is ideal for creating 3D models of objects with intricate surfaces and is commonly used in the art and archaeology industries. However, structured light 3D scanning is less accurate than laser 3D scanning and cannot scan dark surfaces.
Examples of Laser Scanners
Several laser scanners are available in the market today, each with its unique features and specifications. One of the most popular laser scanners is the Faro Focus3D, which is a portable, lightweight scanner that captures high-quality scans in a short amount of time. The scanner offers a range of features, including high-resolution images, sub-millimeter accuracy, and real-time scanning. The Leica Absolute Tracker ATS600 is another popular laser scanner that offers sub-millimeter accuracy and real-time scanning. It is ideal for industrial applications that require high precision and accuracy.
Examples of Structured Light Scanners
Like laser scanners, there are several structured light scanners available in the market. The Artec Eva is a popular structured light scanner that captures high-resolution 3D models in a matter of seconds. The scanner is portable, lightweight, and offers fast scanning and high accuracy. Another popular scanner is the EinScan Pro 2X Plus, which offers high precision, fast scanning speed, and a range of features suitable for industrial and commercial applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both laser 3D scanning and structured light 3D scanning have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which technology to use depends on the specific application and the user’s requirements. Laser 3D scanning is ideal for industries that require high accuracy and precision, while structured light 3D scanning is perfect for capturing surface details. Both technologies have a wide range of applications in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and architecture, among others.
With the continuous development of 3D scanning technology, we can expect to see even more advanced 3D scanners in the future. These scanners will offer higher accuracy, faster scanning speeds, and more features suitable for a range of applications. The 3D scanning technology has revolutionized the way we perceive the world, and with the continuous development, we can expect even more remarkable innovations in the future.