3D printing, a revolutionary technology, has transformed the way we create and manufacture objects. By understanding the 3D printing basics and how it works, you can leverage its numerous applications across various industries. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of 3D printing, its working mechanism, and the diverse applications it offers.
How 3D Printing Works: The Process
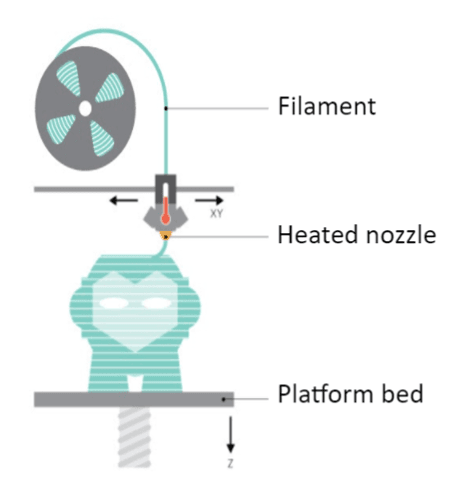
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves the creation of a physical object from a digital model by depositing material layer-by-layer. The process starts with a 3D model designed using computer-aided design (CAD) software or obtained through 3D scanning. The digital model is then sliced into thin layers, which the 3D printer interprets as a series of instructions.
Various 3D printing technologies exist, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technology employs a different approach to depositing and bonding layers of material, but the underlying principle of building objects layer-by-layer remains the same.
3D Printing Applications: Unlocking Potential Across Industries
As the 3D printing basics continue to evolve, its applications are expanding across numerous sectors. Here are some notable examples:
- Manufacturing: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, allowing companies to create and test prototypes quickly and cost-effectively. Moreover, it supports the production of complex, customized parts and facilitates on-demand manufacturing, reducing inventory costs and waste.
- Healthcare: The medical field has greatly benefited from 3D printing. It is now possible to create patient-specific prosthetics, orthotics, and implants with precise fit and functionality. Additionally, 3D bioprinting holds promise for creating tissue and organ replacements.
- Aerospace: 3D printing allows for the production of lightweight and intricate components that can significantly reduce fuel consumption and overall costs in the aerospace industry.
- Automotive: Car manufacturers use 3D printing for rapid prototyping, custom part production, and creating lightweight components, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency.
- Education: 3D printers in educational institutions enable students to engage in hands-on learning experiences, fostering creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills.
- Construction: 3D printing is revolutionizing the construction industry by enabling the creation of affordable, sustainable, and customizable housing solutions.
- Art and design: Artists and designers can use 3D printing to bring their unique creations to life, exploring new forms and materials in their work.
- Fashion: The fashion industry has embraced 3D printing for creating innovative, customized garments, accessories, and even shoes, pushing the boundaries of traditional manufacturing methods.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of 3D Printing
By understanding the 3D printing basics, how it works, and its diverse applications, we can appreciate the transformative impact this technology has across various industries. As advancements in 3D printing continue, the potential for innovation and disruption will only grow, offering new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.