Introduction
Definition of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing stands as an innovative technology revolutionizing the creation of three-dimensional objects from metallic materials, layer by layer, based on a digital model. This process transforms virtual designs into tangible metal products, ushering in a new era for industry and engineering.

The Importance of the Technology in Modern Industry
Metal 3D printing emerges as a crucial catalyst for innovation in industry, facilitating more efficient design and manufacturing of intricate components previously challenging or impossible to produce. This technological leap disrupts conventional manufacturing methods, paving the way for the development of lightweight, durable, and highly functional products.
Metal 3D Printing Technologies
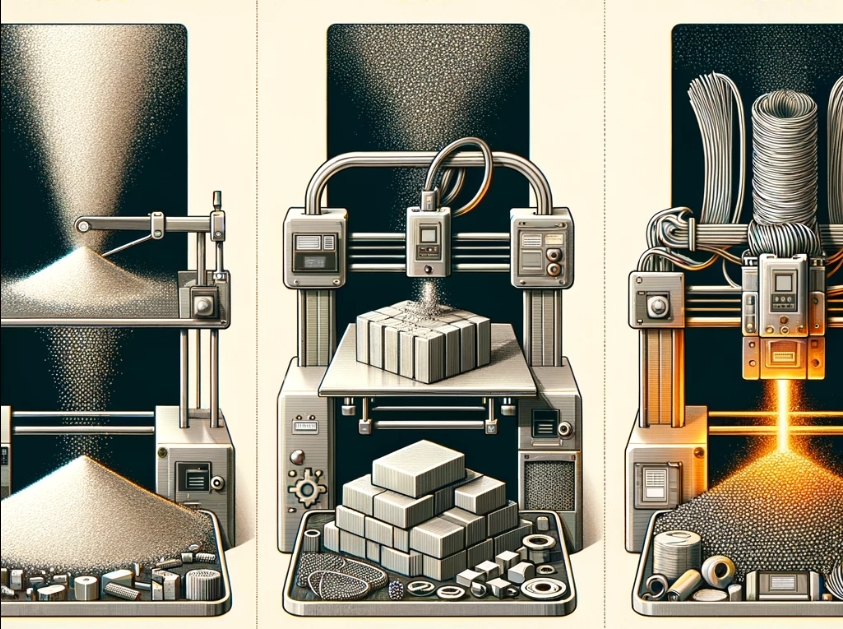
Powder Metal 3D Printing Technologies
Working Principle
Powder metal 3D printing utilizes metal powder distributed in layers on a work surface. A laser or electron beam spot-heats and sinters the powder, creating layers of the product.
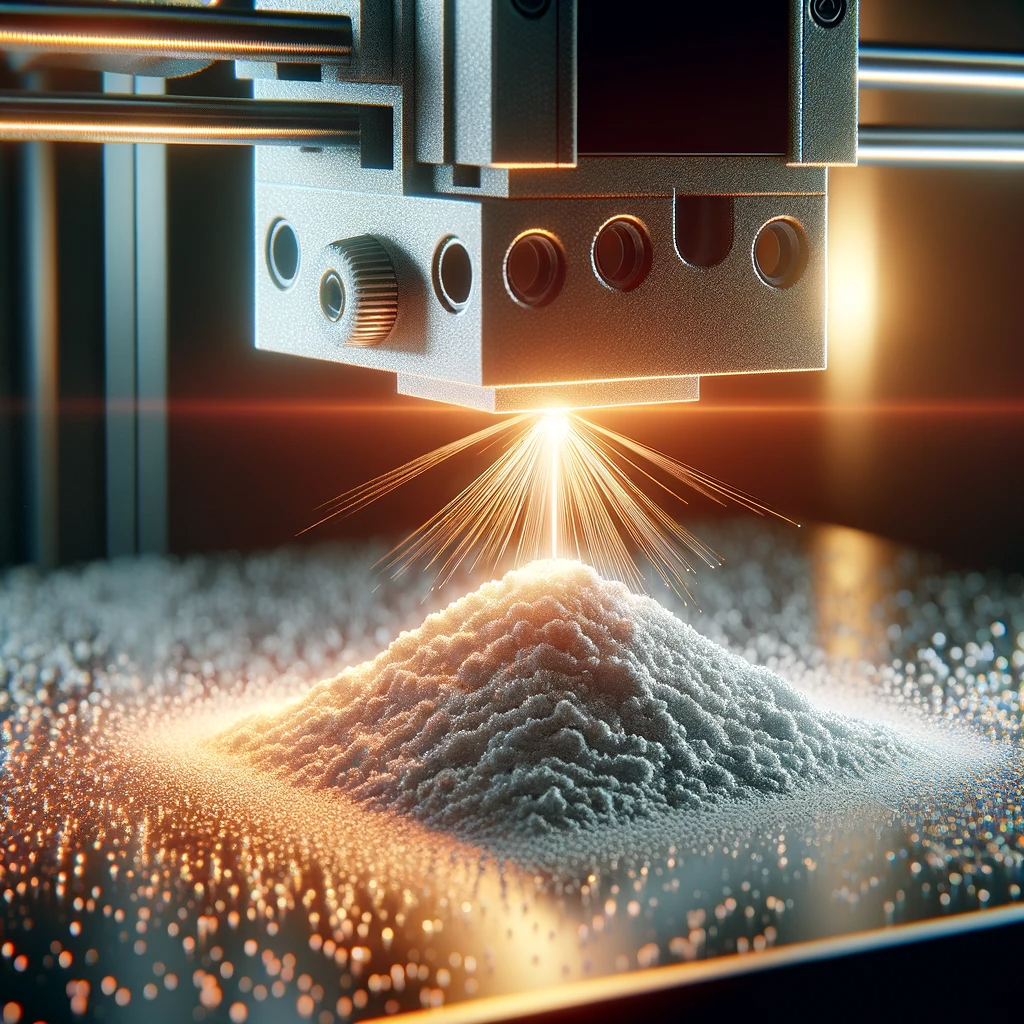
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages include high precision and the ability to form complex structures, but it may be slowed down due to post-print processing and material limitations.
Volumetric Metal 3D Printing
Working Principle
Volumetric metal 3D printing involves surfacing metallic material fed from a special socket, allowing for precise layer-by-layer creation of metal objects.
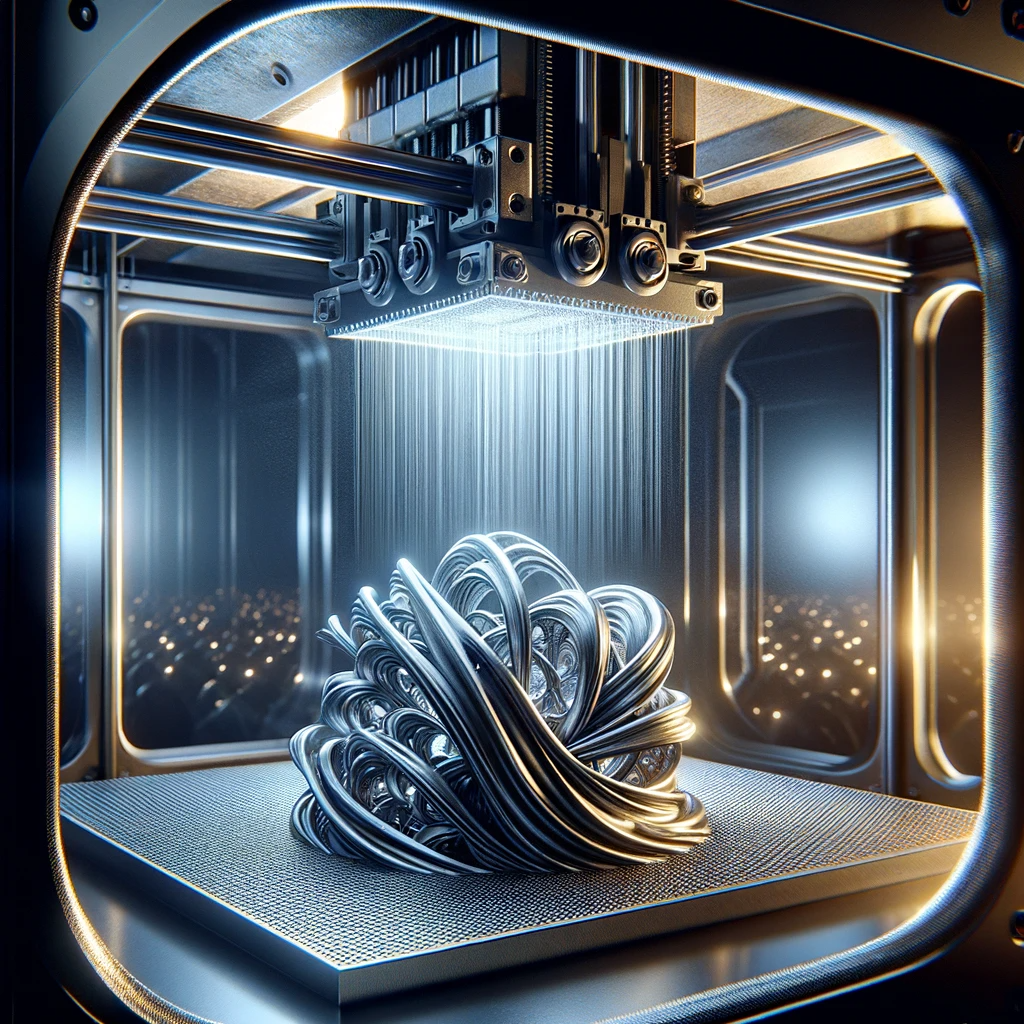
Applications in Various Industries
This technology finds applications in aviation for crafting strong and lightweight components critical to aircraft performance.
Wire Metal 3D Printing
Technical Features
Wire metal 3D printing feeds metal wire through a nozzle, melting and layering it to form three-dimensional objects.
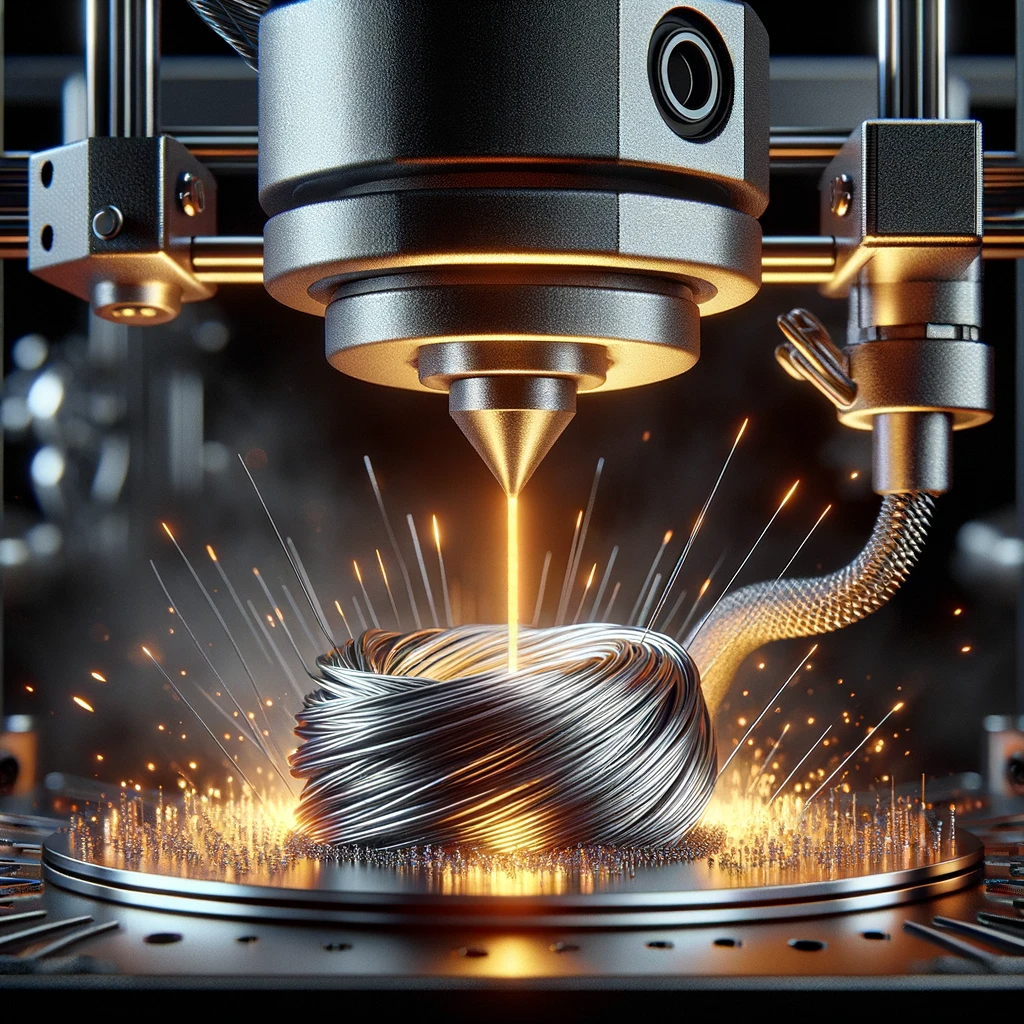

Examples of Successful Applications
Successful applications include the creation of large metal structures like automobile fairings, demonstrating efficiency in producing sizable and durable components.
Applications of Metal 3D Printing
Aerospace Industry
Creating Lightweight and Durable Parts
Metal 3D printing in aviation ensures optimal strength-to-weight ratios for components, critical for fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance.
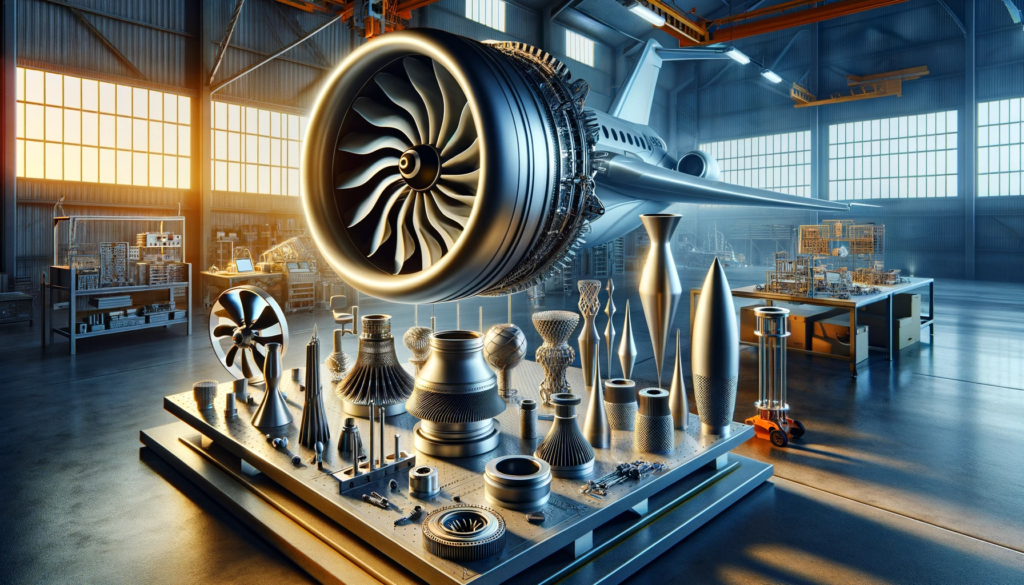

Examples of Successful Projects
Projects such as lightweight turbine blades and structural components for drones showcase the potential in aviation, reducing weight, increasing productivity, and lowering maintenance costs.
Medical Field
Customized Implants
Metal 3D printing revolutionizes the medical field, crafting customized metal implants precisely matching a patient’s anatomy, reducing rejection risks.
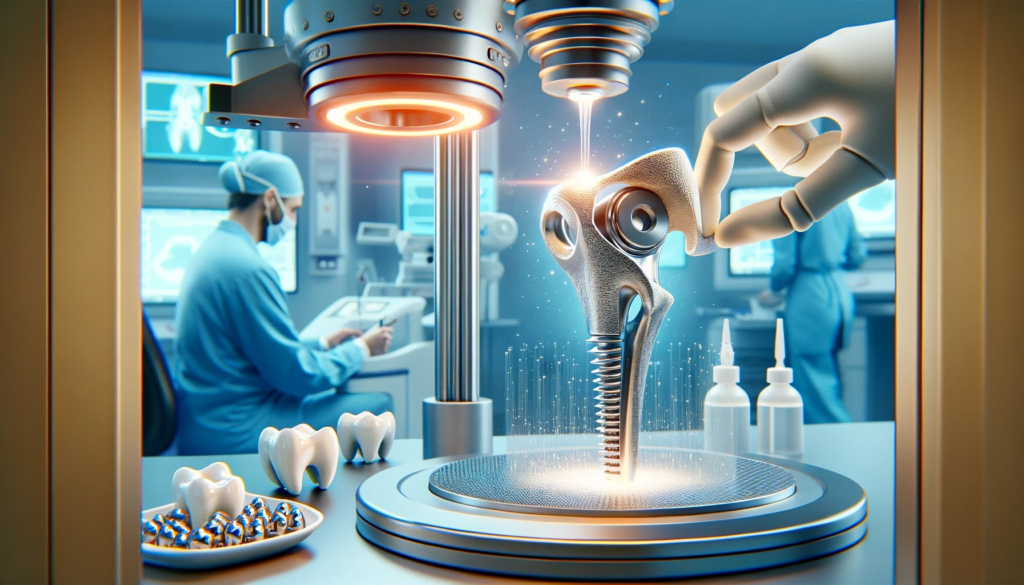

Advances in Dental Prosthetics
The technology finds application in dental prosthetics, allowing for more accurate modeling and providing patients with comfortable and durable solutions.
Automotive Industry
Optimizing Design and Weight of Automotive Parts
Metal 3D printing in the automotive industry optimizes the design and weight of auto parts, creating complex lightweight structures for improved efficiency.
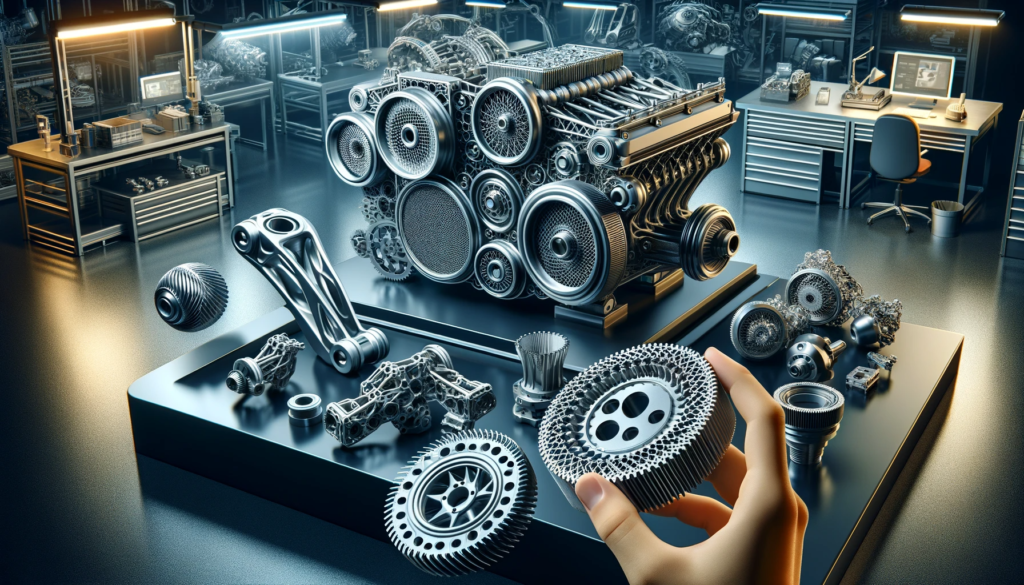
Reduced Production Time
Metal 3D printing significantly reduces the production time of auto parts, crucial in the dynamic automotive industry.
Advantages and Limitations of Metal 3D Printing
Advantages
Customization and Customization
Metal 3D printing enables the creation of unique, customized parts, meeting specific project requirements or customer needs.

Efficient Use of Material
3D printing minimizes material waste, reducing environmental impact and optimizing raw material costs.
Reduced Production Time
Metal 3D printing significantly reduces production time, crucial in fast-paced industries such as aviation and automotive.
Limitations
Technical Challenges
Implementation requires high technical skill, potentially slowing adoption in certain industries.
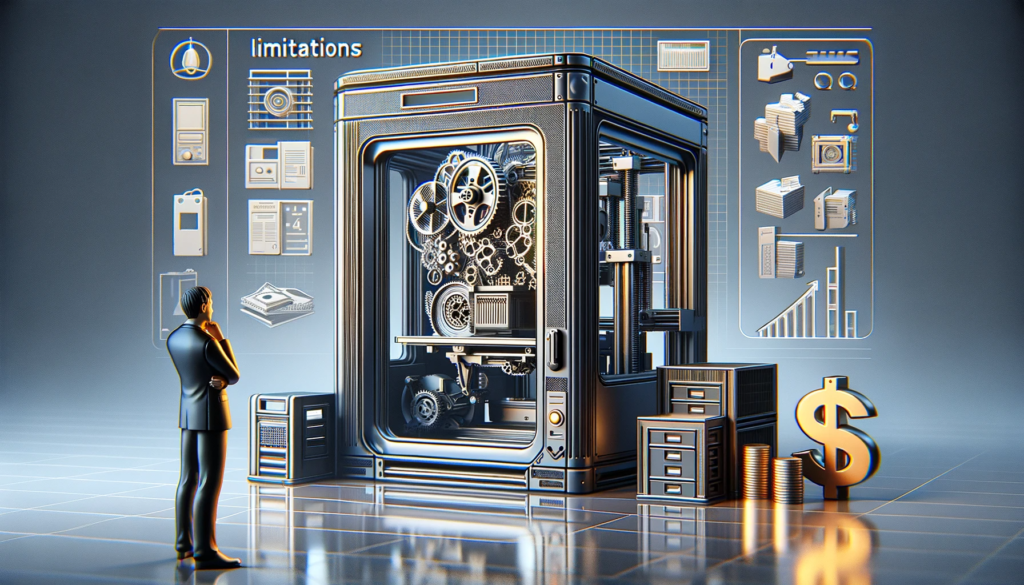
High Equipment Costs
Acquiring and maintaining metal 3D printing equipment requires significant investment, posing challenges for small businesses.
Trends in the Development of Metal 3D Printing
New Materials for 3D Printing
Ongoing research in specialized alloys and composites expands the application boundaries of metal 3D printing, enhancing mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.

Improved Printing Accuracy and Speed
Advancements in technology and control algorithms enhance printing accuracy and speed, contributing to wider adoption across industries.
Integration with Other Technologies
Successful integration with technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the internet of things opens new possibilities for automation, quality control, and innovative solutions.

How to Choose the Right Technology for Your Business
Comparing Different Technologies
Comparing powder, bulk, and wire technologies helps determine their advantages and limitations, aiding in choosing the most suitable for specific tasks.
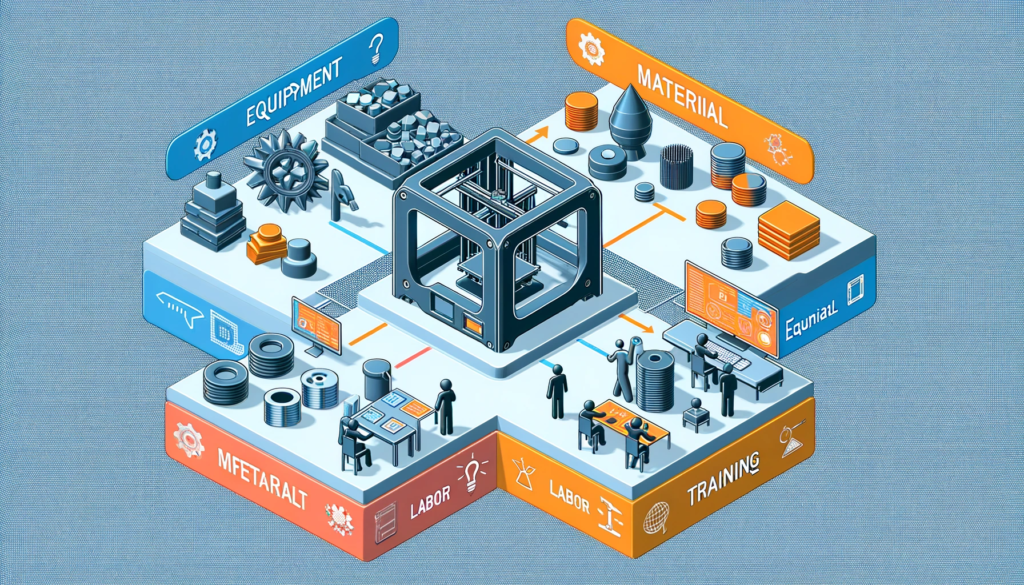
Calculating Cost Effectiveness
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness involves analyzing equipment, material, labor, and training costs for an informed decision.
Examples of Successful Implementation in Various Industries
Examining successful use cases provides valuable insights, inspiring businesses and helping them navigate potential challenges.

Conclusion
Summarizing the Main Points of the Article
Metal 3D printing is transforming manufacturing processes across industries, from aviation to medicine, setting new standards for efficiency and customization.

Prospects for the Development of Metal 3D Printing
Continued technological improvements, expanded material capabilities, and deeper integration with innovative technologies create a favorable environment for the growth of metal 3D printing in the industries of the future.
